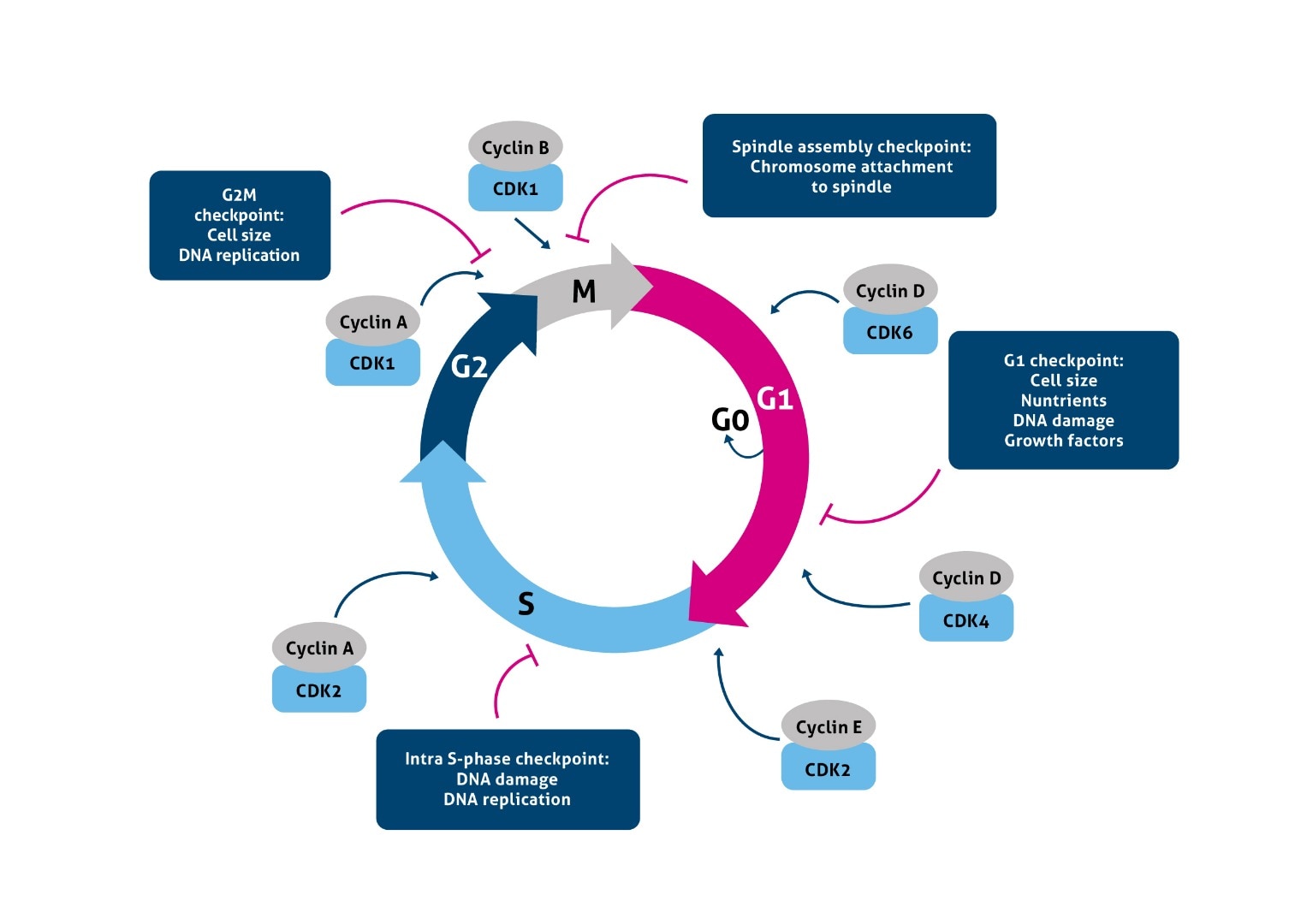
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control . These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. a checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable (e.g. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored by external signals and internal controls called checkpoints. cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell. understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint.
from www.ptglab.com
understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell. each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored by external signals and internal controls called checkpoints. These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. a checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable (e.g. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints.
Cell Cycle and Checkpoint Controls Proteintech Group
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell. each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored by external signals and internal controls called checkpoints. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. a checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable (e.g.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT CHAPTER 12 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2425736 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored by external signals and internal controls called checkpoints. understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From alevelbiology.co.uk
The Cell Cycle Interphase & Mitosis ALevel Biology Revision Notes Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored by external signals and internal controls called checkpoints. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. . Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From biologycellcycles.weebly.com
Mitosis Introduction to Biology The Cell Cycle Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. a checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable (e.g. cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From easybiologyclass.com
Regulation of Cell Cycle by 3 Checkpoints EasyBiologyClass Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control a checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable (e.g. These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. understand how the cell cycle is. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From blog.praxilabs.com
Cell Cycle Regulation Cyclins and CDKs PraxiLabs Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. cell. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From www.ptglab.com
Cell Cycle and Checkpoint Controls Proteintech Group Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell. understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Cell Cycle Control System PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2013694 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored by external signals and internal controls called checkpoints. a checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From www.studocu.com
10 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Cell is controlled in 3 points G1/S, G2/M, and late metaphase Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1,. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From study.com
Cell Cycle Control System Regulators, Purpose & Checkpoints Lesson Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. a checkpoint is one of several points in. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From www.studocu.com
Checkpoints Summary Biology Cell Cycle Control and Checkpoints Although we divide the cell Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 12 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID280824 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell. the cell cycle is controlled at. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From microbenotes.com
Cell Cycle Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. a checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable (e.g. the. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From quizlet.com
Cell Cycle and Checkpoints (in progress) Diagram Quizlet Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. a checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From personalpages.manchester.ac.uk
The cell Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored by external signals and internal controls called checkpoints. a checkpoint is one of several points in the eukaryotic cell cycle at which the progression of a cell to the next stage in the cycle can be halted until conditions are favorable (e.g. understand how the cell cycle is. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From researchtweet.com
Cell Cycle Phases, Diagram, Stage, and Checkpoints Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored by external. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3737558 Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control These checkpoints occur near the end of g 1, at the g 2 /m transition, and during metaphase. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint. cell cycle checkpoints are surveillance mechanisms that monitor the order, integrity, and fidelity of the major events of the cell. each step of the cell cycle is closely. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From www.researchgate.net
Figure No .07 Cell cycle and checkpoint control is an essential target... Download Scientific Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both internal and external to the cell; the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g 1 checkpoint.. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.
From lessonlibraryhauliers.z14.web.core.windows.net
Cell Cycle Checkpoints Explained Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control The integrity of the dna is assessed at the g1 checkpoint. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. each step of the cell cycle is closely monitored by external signals and internal controls called checkpoints. the cell cycle is controlled at three checkpoints. understand how the cell cycle is controlled by mechanisms that are both. Cell Cycle Checkpoints Control.